38 zero coupon bond journal entry
14.3: Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Business LibreTexts Question: This $20,000 zero-coupon bond is issued for $17,800 so that a 6 percent annual interest rate will be earned. As shown in the above journal entry, the bond is initially recorded at this principal amount. Subsequently, two problems must be addressed by the accountant. First, the company will actually have to pay $20,000. How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price - Double Entry Bookkeeping The zero coupon bond price is calculated as follows: n = 3 i = 7% FV = Face value of the bond = 1,000 Zero coupon bond price = FV / (1 + i) n Zero coupon bond price = 1,000 / (1 + 7%) 3 Zero coupon bond price = 816.30 (rounded to 816)
Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - XPLAIND.com A zero-coupon bond is a bond which does not pay any periodic interest but whose total return results from the difference between its issuance price and maturity value. For example, if Company Z issues 1 million bonds of $1000 face value bonds due to maturity in 5 years but which do not pay any interest, it is a zero-coupon bond.
Zero coupon bond journal entry
Journal Entry for Zero Coupon Bonds - Accounting Education Now, we are ready to pass the journal entries of zero coupon bonds. For example, A company issues $ 20,000 zero coupon bond in the market. Mr. David bought it at the discount of $ 3471. It means Mr. David bought it at $ 16529 at 10% per year his earning. At the end of second year, company has to pay only face value of $ 20000. Answered: Assume a firm issues a zero-coupon bond… | bartleby Anatomy and Physiology. Biochemistry. Biology Zero Coupon Bond Issued At Discount Amortization And Accounting Journal ... Accounting for a zero coupon bond issued at a discount (issue price less than face value) interest calculation and balance sheet recording, start with a cas...
Zero coupon bond journal entry. Accounting Deep Discount Bonds - I GAAP & IFRS - CAclubindia A. Zero Coupon Bond (Deep Discount Bond) Zero-coupon bond (also called a discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond issued at a price lower than its face value, with the face value repaid at the time of maturity. It does not make periodic interest payments, or have so-called "coupons," hence the term zero-coupon bond. Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - 2012 Book Archive Prepare journal entries for a zero-coupon bond using the effective rate method. Explain the term "compounding." Describe the theoretical problems associated with the straight-line method, and identify the situation in which this method can be applied. The Issuance of a Zero-Coupon Bond Accounting for Issuance of Bonds (Example and Journal Entry) Suppose ABC company issues a bond at a par value of $ 100,000 and a coupon rate of 5% with 5 years maturity. The market interest rate is also 5%. Let us calculate the PV of bond principal payment and interest component first. PV of bond = $ 100,000 × (0.78355) = $ 78,355. PV Factor 5%, 5 years = 0.78355. Coupon/Interest = $ 100,000 × 5% ... Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia A zero-coupon bond is a debt security instrument that does not pay interest. Zero-coupon bonds trade at deep discounts, offering full face value (par) profits at maturity. The difference between...
Solved On July 1, 2015, ABC Co. issued 10-year, $4,574 ... - Chegg.com Question: On July 1, 2015, ABC Co. issued 10-year, $4,574 million maturity value, 3% coupon bonds when the market rate was 2% for a cash price of $4,994 million. Interest was payable semi-annually on December 31 and June 30. ABC also issued $3,527 million face value, 20-year, zero-coupon bonds on July 1, 2017, that mature June 30, 2037, for a ... Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - GitHub Pages Question: This $20,000 zero-coupon bond is issued for $17,800 so that a 6 percent annual interest rate will be earned. As shown in the above journal entry, the bond is initially recorded at this principal amount. Subsequently, two problems must be addressed by the accountant. First, the company will actually have to pay $20,000. Zero Coupon Bond (Definition, Formula, Examples, Calculations) Zero-Coupon Bond (Also known as Pure Discount Bond or Accrual Bond) refers to those bonds which are issued at a discount to its par value and makes no periodic interest payment, unlike a normal coupon-bearing bond. In other words, its annual implied interest payment is included in its face value which is paid at the maturity of such bond. Convertible zero-coupon bonds - journal entry Hi everyone. I have been given an assignment on convertible zero-coupon bonds. I tried to solve it, but I find it quite difficult and I'd like a review. I hope this is the right place to ask for help on exercises. The data to do this assignment is taken from a real case. I quote the text, which is an excerpt from 2009 report of 3M Company: 3M originally sold $639 million in aggregate face ...
Zero Interest Bonds | Formula | Example | Journal Entry - Accountinguide Please prepare the journal entry during issuing and the annual interest expense. As the company issue bonds at zero interest rate, we need to calculate the selling price first. Selling price = $ 100/ (1+6%)^5 = $ 74.72 Company needs to sell bonds at $ 74.72 per bond. So the company will receive the cash of $ 74,270 for selling 1,000 bonds. 14.3 Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Financial Accounting Question: This $20,000 zero-coupon bond is issued for $17,800 so that a 6 percent annual interest rate will be earned. As shown in the above journal entry, the bond is initially recorded at this principal amount. Subsequently, two problems must be addressed by the accountant. First, the company will actually have to pay $20,000. Malaysian Government Bond: Characters And... | 123 Help Me A zero coupon bond is a bond that makes single payment at its maturity. Examples for zero coupon bonds include Malaysian Treasury Bills (MTB). Malaysian Treasury Bills (MTB) are short term securities issued by the Government of Malaysia. MTBs are used for working capital. MTBs are sold through competitive auction at discount value. Zero Coupon Bonds's Journal Entries | Svtuition Investor gets earning buy getting the zero coupon bonds at discount. This discount will be the income of investor and second side, company has to show it as interest which not in cash but it is the part of face value of zero coupon bonds. I have taught its journal entries in above video.
Journal Entries of Zero Coupon Bonds - YouTube Zero coupon bonds are the famous type of bonds in which the company will gives only face value without paying any extra discount. Investor gets earning buy g...
Journal Entry for Bonds - Accounting Hub Therefore, the journal entry for semiannual interest payment is as follow: This interest payment will start from June 30, 2020, until December 31, 2039. At the maturity date, which is on December 31, 2039, the bonds will need to retire. Thus, ABC Co needs to repay back the principal of the bonds to the bondholders.
Deferred Coupon Bond | Formula | Journal Entry - Accountinguide Company issue 1,000 zero-coupon bonds with a par value of $ 5,000 each. As the bonds do not provide any annual interest to the investors, so they have to be discounted and pay back the full value of par value. The market rate is 5% and the term of the bonds is 4 years. Please calculate the bond price that company needs to sell to attract investors.
14 Bonds.pptx - CHAPTER 14 BONDS AND LONG-TERM NOTES 1 Equity vs Debt 2 ... 15 Journal Entry by the issuer : Journal Entry by the bond investor: CASE 2: ... even interest expenses Zero coupon bonds are usually held by tax-exempt entities such as pension funds. 29 Face Value 10,000 Maturity 5 years Coupon Rate 0% Market Interest Rate 10% Issue price Interest expense over the life of the bond ...
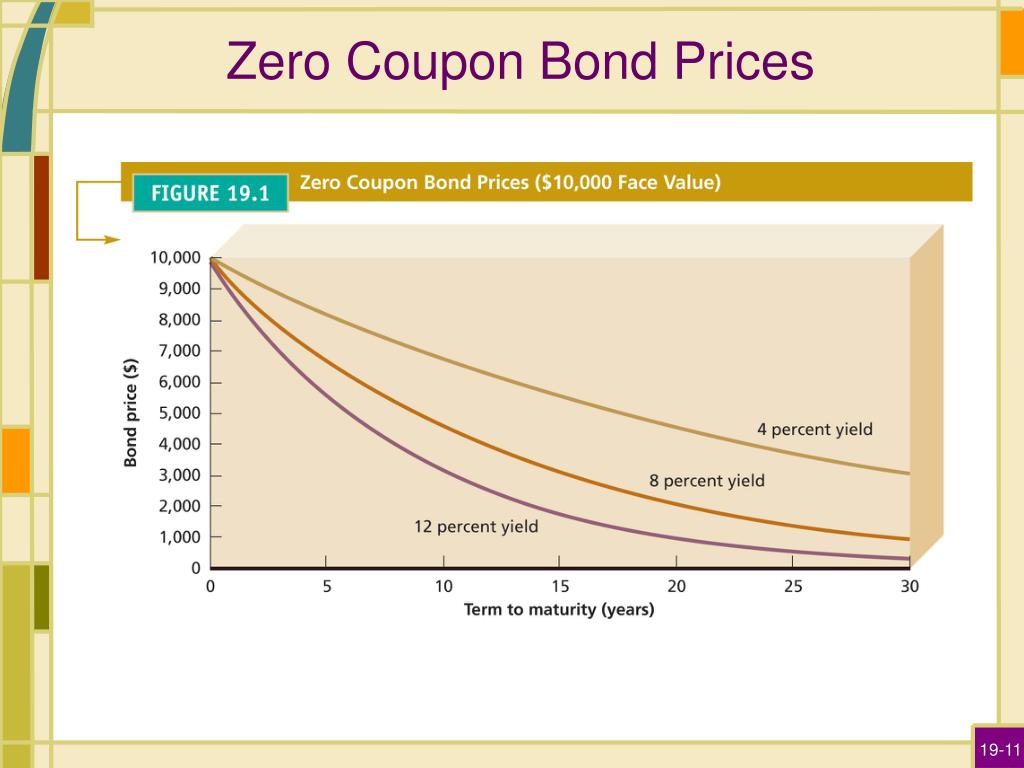

Post a Comment for "38 zero coupon bond journal entry"